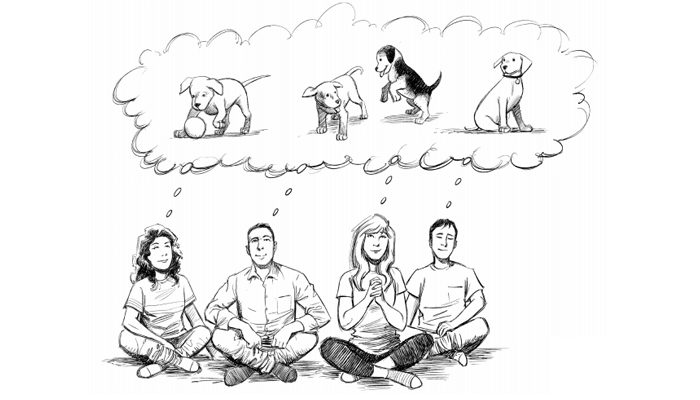
ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽČÓŽĘÓŽżÓŽ« ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż
ÓŽçÓŽëÓŽĆÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽŞ ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽĘÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽĽÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓžŹÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓŽ┐ÓŽŽÓŽ┐ÓŽĘÓŽç ÓŽŞÓžâÓŽťÓŽĘÓŽÂÓžÇÓŽ▓ÓŽĄÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžüÓŽÂÓžÇÓŽ▓ÓŽĘ ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ╣Óžč ÓąĄ ÓŽĽÓŽ┐ÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽĄÓžü ÓŽćÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽŽÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽŞÓžâÓŽťÓŽĘÓŽÂÓžÇÓŽ▓ÓŽĄÓŽżÓžč ÓŽÂÓžłÓŽ▓ÓžŹÓŽ¬ÓŽ┐ÓŽĽÓŽĄÓŽż ÓŽąÓžçÓŽĽÓžç ÓŽČÓŽ┐ÓŽÂÓžŹÓŽ▓ÓžçÓŽĚÓŽúÓŽĘÓŽ┐ÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽşÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓŽż ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžçÓŽĽ ÓŽČÓžçÓŽÂÓŽ┐ ÓąĄ ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ» ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽĘÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽŽÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽĚÓžçÓŽĄÓžŹÓŽ░Óžç ÓŽÂÓžłÓŽ▓ÓžŹÓŽ¬ÓŽ┐ÓŽĽÓŽĄÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽÜÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽÜÓŽż ÓŽ»ÓŽĄÓŽčÓŽż ÓŽŚÓžüÓŽ░ÓžüÓŽĄÓžŹÓŽČÓŽ¬ÓžéÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽú ÓŽćÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽŽÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽĚÓžçÓŽĄÓžŹÓŽ░Óžç ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽŞÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓžÇ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽĄÓŽĄÓŽčÓŽżÓŽç ÓŽŚÓžüÓŽ░ÓžüÓŽĄÓžŹÓŽČÓŽ¬ÓžéÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽú ÓąĄ ÓŽĄÓžüÓŽ«ÓŽ┐ ÓŽ»ÓŽŽÓŽ┐ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽŞÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽĘÓŽż ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽŤ ÓŽĄÓŽżÓŽ╣ÓŽ▓Óžç ÓŽĄÓžüÓŽ«ÓŽ┐ ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘ ÓŽ¬ÓžŹÓŽ░ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽçÓŽëÓŽĆÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽŞ-ÓŽç ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽŤ ÓŽĘÓŽż ÓąĄ
ÓŽŞÓŽČ ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽĘÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽ░ÓŽż ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż ÓŽĘÓŽ┐ÓžčÓžçÓŽç ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽť ÓŽĽÓŽ░Óžç ÓąĄ ÓŽĆÓŽČÓŽé ÓŽşÓŽżÓŽ▓ ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż ÓŽŞÓŽČ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓžčÓŽç ÓŽşÓŽżÓŽ▓ !
ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż ÓŽČÓŽ┐ÓŽşÓžŹÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽĘÓŽ┐ ÓŽ░ÓŽĽÓŽ«ÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽ╣ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░Óžç ÓąĄ ÓŽĽÓŽ┐ÓŽŤÓžü ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż ÓŽĆÓŽ«ÓŽĘ ÓŽĽÓŽ┐ÓŽŤÓžü ÓŽ»ÓŽż ÓŽćÓŽ«ÓŽ░ÓŽż ÓŽČÓŽżÓŽĘÓŽżÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽÜÓŽżÓŽç ÓąĄ ÓŽ»ÓžçÓŽ«ÓŽĘ: ÓŽçÓŽ▓ÓŽ┐ÓŽÂ ÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽŤÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽ«ÓŽ┐ÓŽĚÓžŹÓŽčÓŽ┐ ! (ÓŽ»ÓžçÓŽ╣ÓžçÓŽĄÓžü ÓŽćÓŽ«ÓŽ┐ ÓŽçÓŽ▓ÓŽ┐ÓŽÂ ÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽŤ ÓŽĆÓŽČÓŽé ÓŽ«ÓŽ┐ÓŽĚÓžŹÓŽčÓŽ┐ ÓŽŽÓžüÔÇÖÓŽčÓžőÓŽç ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžçÓŽĽ ÓŽ¬ÓŽŤÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽŽ ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽ┐, ÓŽŽÓžüÓŽčÓžő ÓŽ«ÓŽ┐ÓŽ▓Óžç ÓŽĘÓŽ┐ÓŽÂÓžŹÓŽÜÓžčÓŽç ÓŽĆÓŽ«ÓŽĘ ÓŽĽÓŽ┐ÓŽŤÓžü ÓŽ╣ÓŽČÓžç ÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽíÓŽżÓŽČÓŽ▓ ÓŽ«ÓŽťÓŽż ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽôÓžčÓŽż ÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽČÓžç) ÓąĄ ÓŽĽÓŽ┐ÓŽŤÓžü ÓŽĽÓŽ┐ÓŽŤÓžü ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż ÓŽćÓŽ«ÓŽ░ÓŽż ÓŽČÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽĄÓŽ┐ÓŽŚÓŽĄÓŽşÓŽżÓŽČÓžç ÓŽľÓžüÓŽČÓŽç ÓŽ¬ÓŽŤÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽŽ ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽ┐ ÓąĄ ÓŽ»ÓžçÓŽ«ÓŽĘ: ÓŽÜÓžőÓŽľÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽşÓžŹÓŽ░ÓžüÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽĆÓŽĽ ÓŽíÓŽťÓŽĘ ÓŽ░ÓŽ┐ÓŽé ÓŽ¬ÓžťÓŽż ÓąĄ ┬áÓŽćÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓŽ┐ÓŽŤÓžü ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż ÓŽ╣ÓŽ▓Óžő ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽŞÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽĽÓŽ░Óžç ÓąĄ ÓŽćÓŽ░ ÓŽĆÓŽç ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽŞÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽżÓŽç ÓŽ╣ÓŽ▓Óžő ÓŽçÓŽëÓŽĆÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽŞ ÓąĄ
ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ»ÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽŤÓžç ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓžÇ ÓŽô ÓŽůÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽąÓŽ¬ÓžéÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽúÓŽşÓŽżÓŽČÓžç ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽŞÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽĽÓŽ░Óžç ÓŽĆÓŽ«ÓŽĘ ÓŽĽÓŽ┐ÓŽŤÓžüÓŽç ÓŽ╣ÓŽ▓Óžő ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż ÓąĄ
ÓŽ»ÓžçÓŽľÓŽżÓŽĘÓžç ÓŽÂÓŽ┐ÓŽ▓ÓžŹÓŽ¬ÓžÇ ÓŽĆÓŽČÓŽé ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ» ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽĘÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽ░ÓŽż ÓŽĘÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽ«ÓŽĄÓžő ÓŽĽÓŽ░Óžç ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽĘ ÓŽĽÓŽ░Óžç, ÓŽçÓŽëÓŽĆÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽŞ ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽĘÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽ░ÓŽż ÓŽĽÓŽ░Óžç ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓžŹÓŽ¬ÓžéÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽú ÓŽĄÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽČÓŽ┐ÓŽ¬ÓŽ░ÓžÇÓŽĄ ÓŽ¬ÓŽŽÓžŹÓŽžÓŽĄÓŽ┐ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽĆÓŽČÓŽé ÓŽëÓŽŽÓžŹÓŽŽÓžçÓŽÂÓžŹÓŽ»Óžç ÓąĄ ÓŽĄÓžőÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽĽÓžç ÓŽŞÓžâÓŽťÓŽ┐ÓŽĘÓŽÂÓžÇÓŽ▓ÓŽĄÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽÜÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽÜÓŽż ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ╣ÓŽČÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓžŹÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓŽ┐ÓŽĘÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽĄ ÓąĄ ÓŽČÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽČÓŽ╣ÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽ░ÓžÇÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽŤÓžç ÓŽĄÓžőÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż ÓŽ¬ÓŽŤÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽŽÓŽŞÓŽç ÓŽČÓŽż ÓŽůÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽąÓŽ¬ÓžéÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽú ÓŽĘÓŽż ÓŽ╣ÓŽ▓Óžç ÓŽŞÓžçÓŽç ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘ ÓŽ«ÓžéÓŽ▓ÓžŹÓŽ» ÓŽČÓŽż ÓŽ¬ÓžŹÓŽ░ÓžčÓžőÓŽťÓŽĘÓžÇÓžčÓŽĄÓŽż ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘÓŽčÓŽżÓŽç ÓŽĘÓžçÓŽç ÓąĄ ÓŽŞÓžçÓŽčÓŽż ÓŽĄÓžőÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽ»ÓŽĄ ÓŽ¬ÓŽŤÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽŽÓŽŞÓŽç ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽżÓŽç ÓŽ╣ÓžőÓŽĽ ÓŽĘÓŽż ÓŽĽÓžçÓŽĘ ÓąĄ
ÓŽĆÓŽ░ ÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽĘÓžç ÓŽ╣ÓŽ▓Óžő ÓŽĄÓžőÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽĆÓŽ«ÓŽĘ ÓŽŞÓŽČ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽŞÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽż ÓŽĘÓŽ┐ÓžčÓžç ÓŽşÓŽżÓŽČÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ╣ÓŽČÓžç, ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽť ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ╣ÓŽČÓžç ÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽŞÓŽżÓŽąÓžç ÓŽĄÓžőÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽĘÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓžŹÓŽ¬ÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽĽ ÓŽĘÓžçÓŽç ÓąĄ ÓŽ¬ÓžŹÓŽ░ÓŽąÓŽ«ÓŽŽÓŽ┐ÓŽĽÓžç ÓŽČÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽčÓŽż ÓŽĆÓŽĽÓŽčÓžü ÓŽŚÓžőÓŽ▓ÓŽ«ÓžçÓŽ▓Óžç ÓŽ«ÓŽĘÓžç ÓŽ╣ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░Óžç ÓąĄ ÓŽćÓŽ░ ÓŽĆ ÓŽťÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽç ÓŽçÓŽëÓŽĆÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽŞ ÓŽľÓžüÓŽČ ÓŽŞÓžŹÓŽČÓŽĄÓŽúÓžŹÓŽĄÓžŹÓŽ░ ÓŽĆÓŽČÓŽé ÓŽ«ÓžéÓŽ▓ÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽČÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽČÓŽż ÓŽŚÓžüÓŽ░ÓžüÓŽĄÓžŹÓŽČÓŽ¬ÓžéÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽú ÓŽĆÓŽĽÓŽčÓŽż ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽť: ÓŽŽÓžüÓŽ░ÓžéÓŽ╣ ÓŽĄÓžő ÓŽČÓŽčÓžçÓŽç ÓąĄ
ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽ╣ÓŽ▓Óžő ÓŽćÓŽçÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓžčÓŽż ÓŽ»ÓŽż ÓŽşÓžüÓŽ▓ ÓŽ¬ÓžŹÓŽ░ÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽúÓŽ┐ÓŽĄ ÓŽ╣ÓŽĄÓžçÓŽç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░Óžç ÓąĄ ÓŽĆ ÓŽĘÓŽ┐ÓžčÓžç ÓŽŽÓžüÓŽâÓŽľ ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓŽ┐ÓŽŤÓžü ÓŽĘÓžçÓŽç ÓąĄ
ÓŽçÓŽëÓŽĆÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽŞ ÓŽĆ ÓŽćÓŽ«ÓŽ░ÓŽż ÓŽ¬ÓŽ░ÓžÇÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽĚÓŽż-ÓŽĘÓŽ┐ÓŽ░ÓžÇÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽĚÓŽż ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽ┐ ÓąĄ ÓŽĆÓŽĽÓŽç ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽŞÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžçÓŽĽÓŽŚÓžüÓŽ▓Óžő ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽČÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽ┐ ÓŽĆÓŽČÓŽé ÓŽĄÓŽżÓŽŽÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽ¬ÓžŹÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓžŹÓŽ»ÓžçÓŽĽÓŽčÓŽ┐ÓŽĽÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽ░ÓžÇÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽĚÓŽż ÓŽĽÓŽ░Óžç ÓŽŽÓžçÓŽľÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽ┐ ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘÓŽčÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽÜÓžçÓžčÓžç ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘÓŽčÓŽż ÓŽşÓŽżÓŽ▓ ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽť ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽŤÓžç ÓąĄ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽ╣ÓŽ┐ÓŽŞÓžçÓŽČÓžç ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘÓŽčÓŽż ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽŚÓžüÓŽ▓ÓžőÓŽ░ ÓŽąÓžçÓŽĽÓžç ÓŽşÓŽżÓŽ▓ ÓŽĆÓŽČÓŽé ÓŽëÓŽ¬ÓŽ»ÓžüÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽĄ ÓąĄ ÓŽĆÓŽ«ÓŽĘÓŽĽÓŽ┐ ÓŽČÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽČÓŽ╣ÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽĽÓŽżÓŽ░ÓžÇÓŽĽÓžç ÓŽťÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓžŹÓŽ×ÓžçÓŽŞ ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽ┐ ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘÓŽčÓŽż ÓŽĄÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽëÓŽ¬ÓŽ»ÓžüÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽĄ ÓŽô ÓŽ¬ÓŽŤÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽŽ ÓŽ╣ÓžčÓžçÓŽŤÓžç ÓąĄ
ÓŽĆÓŽ░ ÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽĘÓžç ÓŽ╣ÓŽ▓Óžő ÓŽçÓŽëÓŽĆÓŽĽÓžŹÓŽŞ ÓŽĆÓŽĽÓŽčÓŽ┐ ÓŽČÓŽ┐ÓŽÂÓžçÓŽĚ ÓŽžÓŽ░ÓŽĘÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽĘ: ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽĘÓŽčÓŽ┐ ÓŽşÓžüÓŽ▓ ÓŽ╣ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░Óžç ÓąĄ ÓŽĆÓŽČÓŽé ÓŽćÓŽ«ÓŽ░ÓŽż ÓŽ¬ÓžŹÓŽ░ÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽú ÓŽĽÓŽ░ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░ÓŽ┐ ÓŽ»Óžç ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽčÓŽ┐ ÓŽşÓžüÓŽ▓ ÓŽ╣ÓžčÓžçÓŽŤÓžç ÓąĄ ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ» ÓŽÂÓžłÓŽ▓ÓžŹÓŽ¬ÓŽ┐ÓŽĽ ÓŽíÓŽ┐ÓŽťÓŽżÓŽçÓŽĘÓžç ÓŽĄÓŽżÔÇÖ ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓžŹÓŽşÓŽČ ÓŽĘÓŽż ÓąĄ
ÓŽĆÓŽĽÓŽç ÓŽŞÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽžÓŽżÓŽĘ ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘ ÓŽŞÓŽżÓŽçÓŽčÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽťÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ» ÓŽŞÓŽáÓŽ┐ÓŽĽ ÓŽ╣ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░Óžç ÓŽćÓŽČÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽůÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ» ÓŽĽÓžőÓŽĘ ÓŽŞÓŽżÓŽçÓŽčÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽťÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ» ÓŽşÓžüÓŽ▓ ÓŽ¬ÓŽ░ÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽČÓŽÂÓŽ┐ÓŽĄ ÓŽ╣ÓŽĄÓžç ÓŽ¬ÓŽżÓŽ░Óžç ! ÓŽčÓžüÓŽçÓŽčÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽĆÓŽ░ ÓŽĆÓŽç ÓŽźÓŽ┐ÓŽÜÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽľÓžüÓŽČ ÓŽČÓŽ┐ÓŽľÓžŹÓŽ»ÓŽżÓŽĄ ÓŽĆÓŽČÓŽé ÓŽşÓŽżÓŽ▓ ÓŽČÓŽ▓ÓžçÓŽç ÓŽ»Óžç ÓŽĄÓŽż ÓŽĄÓžőÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽ░ ÓŽŞÓŽżÓŽçÓŽčÓžçÓŽ░ ÓŽťÓŽĘÓžŹÓŽ» ÓŽ«ÓŽżÓŽĘÓŽżÓŽĘÓŽŞÓŽç ÓŽ╣ÓŽČÓžç ÓŽĄÓŽżÔÇÖ ÓŽĆÓŽĽÓžçÓŽČÓŽżÓŽ░ÓžçÓŽç ÓŽáÓŽ┐ÓŽĽ ÓŽĘÓŽż ÓąĄ